A Technical Overview for Industrial Manufacturing
Roll forming is a continuous metal shaping process where flat steel coils are gradually bent into specific cross-sectional profiles through a series of roll stations. This method is widely used in industries that demand high precision, structural strength, and consistent quality, including construction, automotive, solar mounting systems, and industrial equipment production.
At Lotosforming, advanced solutions are designed to handle various steel types while ensuring strict tolerances and efficient production.
Steel Materials Used
Roll forming can process multiple steel materials, chosen based on strength, corrosion resistance, and end-use requirements:
Carbon Steel (Mild to High Strength)
Galvanized Steel (GI / HDG)
Pre Painted Steel (PPGI / PPGL)
Stainless Steel
High Strength Low-Alloy Steel (HSLA)
Typical thickness ranges from 0.5 mm to 8.0 mm, depending on application and machinery.
Roll Forming Process for Steel
The roll forming steel process consists of multiple technical stages:
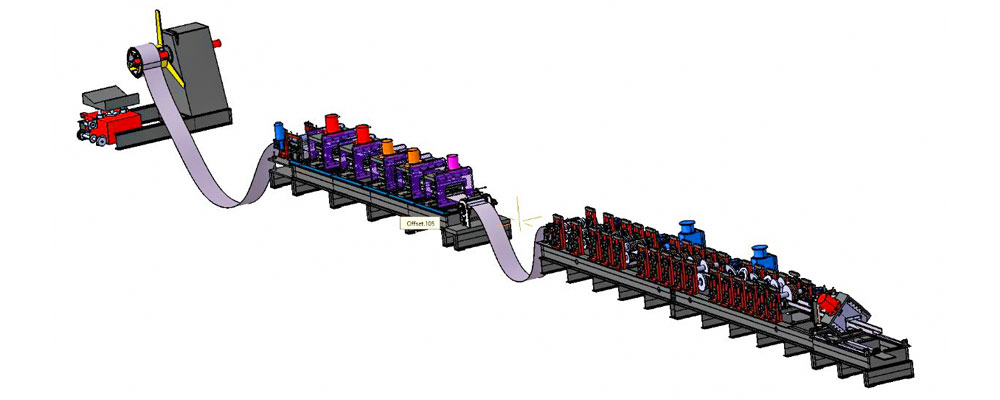
1. Coil Feeding and Leveling
Steel coils are loaded onto a decoiler and passed through a precision leveling system to remove residual stresses and flatness deviations.
2. Progressive Roll Forming Stations
Each roll station incrementally bends the steel strip, minimizing material strain and preventing surface damage. The number of stations is determined by:
Profile complexity
Steel thickness
Yield strength of the material
3. Punching and Slotting (Optional)
Inline hydraulic or servo punching systems can be integrated for holes, slots, or embossing without interrupting production speed.
4. Cut to Length System
Flying shear or stop to cut systems ensure accurate length control with minimal burr formation.
Technical Advantages of Roll Forming Steel
Roll forming steel offers several engineering and production benefits:
High dimensional precision and repeatability
Excellent surface finish preservation
Low material waste compared to stamping
High production speed for mass manufacturing
Consistent mechanical properties along the profile length
These advantages make roll forming steel ideal for long length profiles and structural components.
Design Considerations in Steel Roll Forming
Successful roll forming of steel requires careful engineering of:
Roll tooling geometry
Forming angle progression
Springback compensation
Roll material hardness
Drive system torque capacity
Advanced CAD/CAM and simulation software are commonly used to optimize roll design and reduce trial adjustments.
Applications of Roll Formed Steel Products
Roll forming steel is extensively applied in:
Solar mounting structures
Steel framing and purlins
Cable trays and ladder systems
Automotive structural components
Warehouse racking systems
Industrial enclosures and panels
Lotosforming machines are designed to meet international standards for structural and industrial steel applications.
Automation and Control Systems
Modern roll forming steel lines incorporate:
PLC based control systems
Servo driven feeding and punching
Automated profile changeover
Real time production monitoring
These technologies enhance production efficiency, reduce downtime, and improve overall product consistency.
Roll Forming in Sheet Metal Forming
Roll forming steel is a highly efficient and technically advanced manufacturing process for producing precise, durable, and high quality steel profiles. With its ability to process various steel grades at high speed and low waste, roll forming remains a preferred solution for large scale industrial production.
FAQ:
Common materials include mild steel, galvanized steel, pre painted steel (PPGI), stainless steel, and high strength steel (HSLA), depending on the application.
Yes, Lotosforming provides fully customizable profiles, dimensions, and materials to meet specific project requirements.
Roll forming steel is a continuous cold forming process where steel coils pass through a series of precision rollers to create uniform profiles with consistent shapes and high dimensional accuracy.
Key benefits include high production speed, low material waste, excellent dimensional consistency, smooth surface finish, and the ability to produce complex profiles.
